 |
Two-loop windmill for stable energy supply Project substantiation p. 1 |
 |
ōAs price on electricity permanently grows, alternative sources of energy already do not seem phantasmal ideas of inventors. If we add market conditions, we will understandö [1] that energetic resources have to be developed towards environmentally safe sources ¢ vegetable-oil fuel and energy of sun and wind. Experts say, resources of wind energy are about ō170 trillion kW/hour yearly, and we can obtain this energy, doing not soiling the environmentö [1]. This is why scientific and industrial experts and power engineers all over the world address to discover effective electric power stations that use the energy of wind. They develop mainly three trends:
|
Fig. 1
|
¢ create low-power windmills able to supply with energy remote separate houses and farms; their power is from 300 W to 5 ¢ 20 kW [2], [3]; |
Fig. 2
|
¢ create medium-power windmills able to supply with energy remote small villages and farms, their power is from 20 to 500-600 kW [4]; |
Fig. 3
|
¢ create powerful windmills, above 1 Megawatt [5], [6]. |
|
All types of windmills are based on general principle: ōA windmill consists of a bladed wheel, a generator, a direct-to-alternating current converter and a storage battery. It works simply: the wind rotates the bladed wheel passing the torque through the reduction gear to the shaft of generator. So the mechanical energy turns into that electricö [1], though as power grows, the construction sufficiently complicates. First windmills had two constructions ¢ vane- and fan-type. As a rule, these first were used for low-power mills and these second for bigger, though in the beginning they were not strongly divided. For example, the first powerful windmill built in Denmark in 1890 had three blades [1], see Fig. 4a. The first Russian windmills built in the end of 19th century were both fan- (Fig. 4b) and vane-type [7].
|
a |
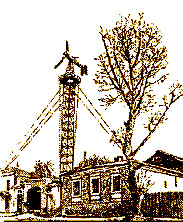 b |
 c |
Fig. 4
|
|
The vane type is also used now for low-power windmills ¢ for example, to elevate water from wells (see Fig. 5 a and b). |
a |
 b |
 c |
Fig. 5
|
|
The sail-type windmill Silver Scat (Fig. 5c) is a developed kind of such windmills [9] |
--------------------------------------
Journal of laboratory Business-plan Substantiation of project